Palm trees, with their stately presence and graceful fronds, are a common sight in tropical and subtropical regions. But beyond their aesthetic appeal, these trees possess a fascinating anatomy that plays a crucial role in their growth and survival.
Understanding palm tree anatomy is essential for proper identification, cultivation, and appreciation of these magnificent plants.
A Comprehensive Guide to Palm Tree Anatomy
This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of palm tree anatomy, covering key structures, their functions, and historical significance.
The guide is structured to address various aspects of palm tree anatomy, including the palm tree trunk, roots, and leaves. It also delves into the hidden secrets and cultural significance of these trees.
Palm Tree Trunk: Structure and Functions
The palm tree trunk, also known as the stem, is a unique and distinguishing feature of palm trees. Unlike most trees, which have a woody trunk, the palm tree trunk is made up of tightly packed leaf bases. This distinctive structure gives it a characteristic fibrous texture.
The palm tree trunk provides structural support, allowing the tree to withstand strong winds and storms. It also serves as a water reservoir, storing water and nutrients for use during dry periods.

FREE Printable Tree Trunk Diagram Activity in 2021 | Homeschool nature – Source www.pinterest.com
Palm Tree Roots: Anchorage and Nutrient Absorption
Palm tree roots are equally fascinating. They are typically fibrous and spreading, providing a strong and stable foundation for the tree. The roots extend far and wide, anchoring the tree firmly in the ground and absorbing water and nutrients from a large area.
The palm tree’s extensive root system also helps prevent erosion and soil compaction.

Outdoor Interpretive Sign: Tree, Anatomy, Parts, Illustration, Diagram – Source www.pulsedesign.com
Palm Tree Leaves and Crown: Photosynthesis and Reproduction
Palm tree leaves are usually large and pinnately compound, giving them their characteristic feathery appearance. These leaves are arranged in a crown at the top of the tree and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which the tree converts sunlight into energy.
The crown of the palm tree is also where reproduction takes place. Palm trees produce flowers and fruits, which are often clustered in inflorescences.
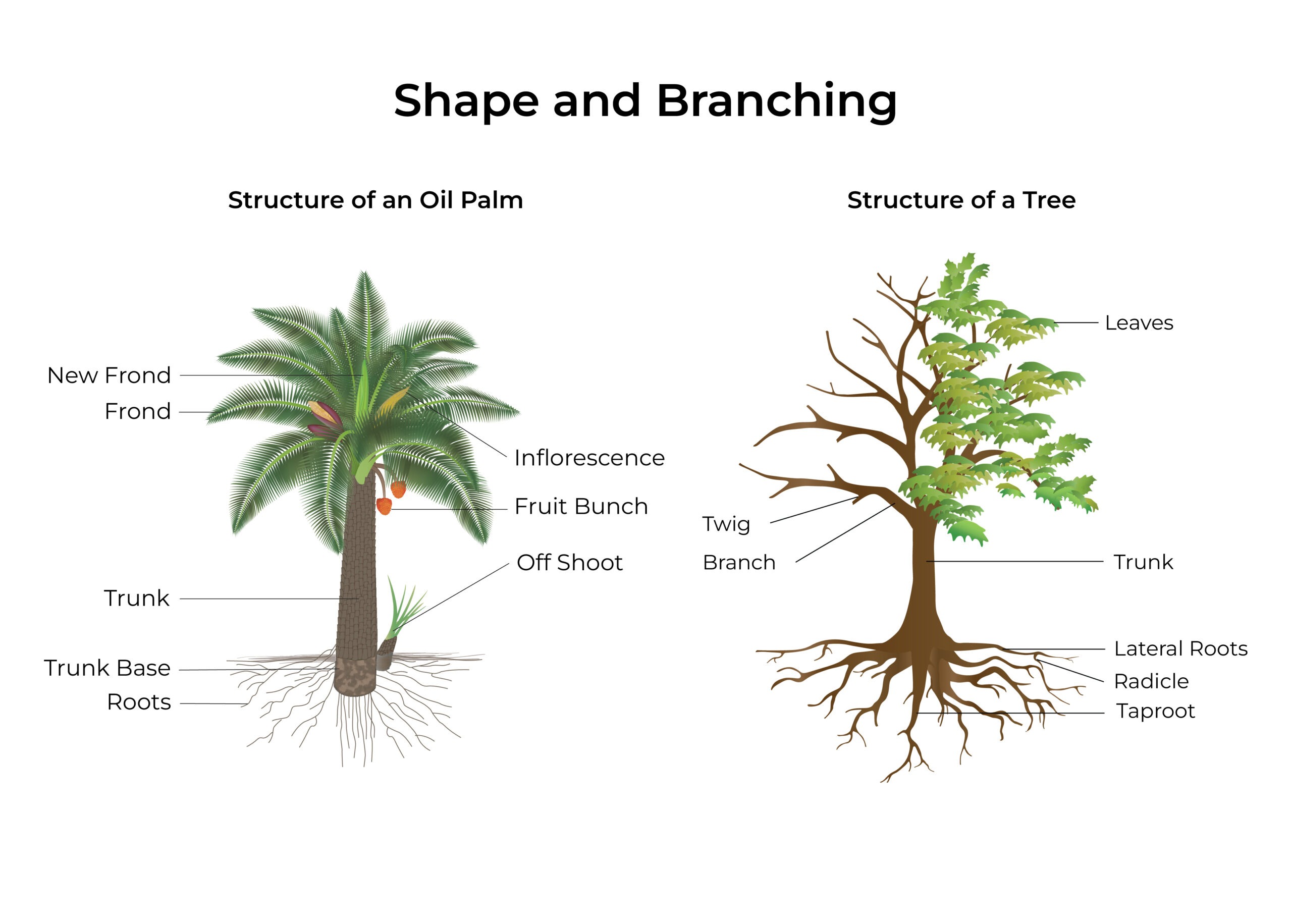
Oil Palm Anatomy: 5 Ways an Oil Palm Differs From a Typical Tree – Source www.musimmas.com
Cultural Significance of Palm Trees
Palm trees have been revered in many cultures throughout history. In ancient Egypt, the palm tree was associated with the god Thoth, the patron of wisdom and writing.
In Christianity, palm fronds are a symbol of victory and were used to welcome Jesus into Jerusalem.

PDNS Tree and Leaf Identification Guide Parts of Tree Anatomy Outdoor – Source www.pulsedesign.com
Hidden Secrets of Palm Tree Anatomy
Beyond their visible structures, palm trees hold some hidden secrets. For instance, did you know that the trunk of a palm tree is actually a giant stem? It is composed of a mass of fibrous tissue called parenchyma and does not contain any true wood.
Another fascinating fact is that palm trees are monocotyledons, meaning they have a single seed leaf.
Recommended Resources for Palm Tree Anatomy
There are several excellent resources available for those interested in exploring palm tree anatomy in more detail.
The book “The Palm Tree: A Comprehensive Guide” by John Dransfield and Natalie Uhl provides a comprehensive overview of palm tree anatomy, biology, and cultivation.

Outdoor Interpretive Sign: Tree, Anatomy, Parts, Illustration, Diagram – Source www.pulsedesign.com
Historical Perspectives on Palm Tree Anatomy
Palm trees have been studied and documented for centuries. Early explorers and naturalists were intrigued by these unique plants and made detailed observations of their anatomy.
In the 18th century, the Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus developed a classification system for palm trees based on their floral characteristics. This system laid the foundation for modern palm tree taxonomy.
Tips for Identifying Palm Tree Anatomy
Identifying palm tree anatomy can be challenging, especially for beginners. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
- Observe the leaf shape, size, and arrangement.
- Examine the trunk for its texture, color, and presence of leaf scars.
- Inspect the roots for their type (fibrous or taproot) and spread.
- Consider the overall size and shape of the tree.
- Refer to field guides or consult with a botanist for expert identification.
Bronchial Tree Anatomy Diagram – Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
Fun Facts about Palm Tree Anatomy
Did you know that the world’s tallest palm tree is the wax palm, which can reach heights of over 200 feet?
Another fascinating fact is that palm trees are fire-resistant, thanks to their high water content and thick bark.
Conclusion of Comprehensive Palm Tree Anatomy Diagram For Identification And Understanding
Understanding palm tree anatomy is not only essential for proper identification but also for appreciating the unique adaptations and beauty of these remarkable plants.
Whether you are a botanist, a gardener, or simply an admirer of nature, we hope this guide has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of palm tree anatomy and its significance.