Palm trees are iconic symbols of tropical paradise, but did you know that they also have a fascinating anatomy that plays a vital role in their survival? Let’s dive deep into the complete guide to palm tree anatomy to uncover the secrets behind these majestic trees.

The anatomy of an oil palm | Focus on Arts and Ecology – Source nghethuatvasinhthai.blogspot.com
Key Parts of a Palm Tree
Palm trees have a unique structure that distinguishes them from other trees. The main components include:
- Trunk: The trunk is the main stem of the palm tree, providing support and transporting nutrients. It is usually unbranched and has a distinct ringed pattern.
- Crown: The crown is the topmost part of the palm tree, consisting of a cluster of leaves. It is responsible for photosynthesis and provides shade.
- Leaves: Palm tree leaves are large and often fan-shaped or feather-like. They play a crucial role in capturing sunlight and producing food for the tree.
- Roots: The root system of palm trees is extensive and fibrous, anchoring the tree firmly in the ground and absorbing water and nutrients.
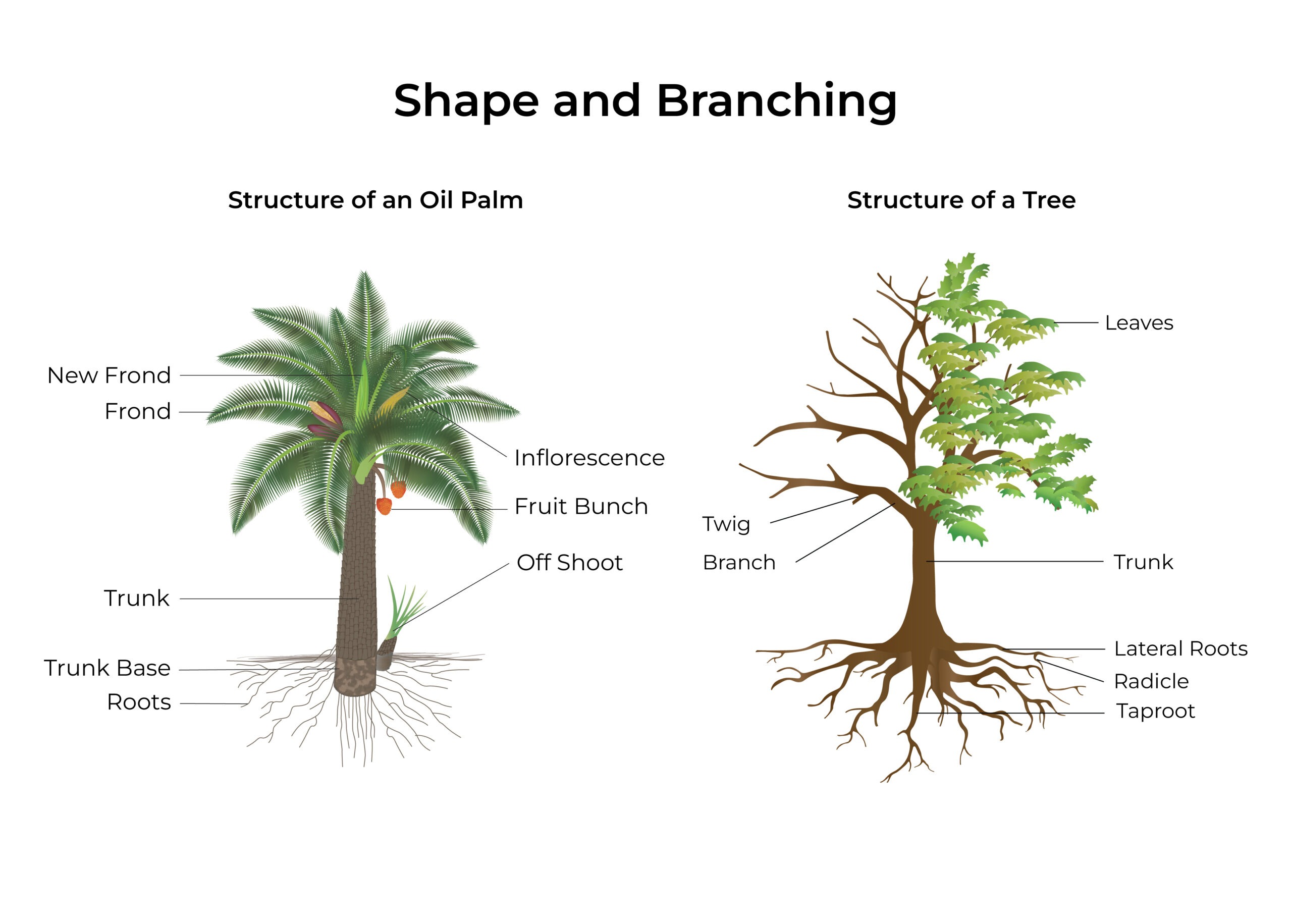
Oil Palm Anatomy: 5 Ways an Oil Palm Differs From a Typical Tree – Source www.musimmas.com
Functions of Palm Tree Anatomy
Each part of the palm tree anatomy serves specific functions that contribute to the tree’s growth and survival:
- Trunk: The trunk supports the weight of the crown and provides a pathway for the movement of water and nutrients.
- Crown: The crown absorbs sunlight and converts it into energy through photosynthesis. It also provides shade and protection from wind and rain.
- Leaves: The leaves are the primary photosynthetic organs of the palm tree, capturing sunlight and producing food through chlorophyll.
- Roots: The roots anchor the tree in the ground, preventing it from toppling over. They also absorb water and essential nutrients from the soil.

Parts Of An Animal Cell And Their Functions – Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
History and Myth of Palm Trees
Palm trees have a rich history and cultural significance. They have been revered in many cultures for their beauty, symbolism, and practical uses. In ancient Egypt, palm trees were associated with the goddess Isis and were often depicted in hieroglyphics. In Christianity, the palm branch is a symbol of victory and peace, as it was used by Jesus on his triumphal entry into Jerusalem. Palm trees have also been used for centuries to produce various products, including food, oil, and building materials.
Bronchial Tree Anatomy Bronchoscopy – Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
Hidden Secrets of Palm Trees
Beyond their visible anatomy, palm trees hold hidden secrets that contribute to their resilience and adaptability. For example, palm trees have the ability to store water in their trunks, which helps them survive in arid conditions. Additionally, their leaves have a waxy coating that protects them from excessive water loss through evaporation. These hidden adaptations allow palm trees to thrive in diverse environments.
Recommendations for Growing Palm Trees
To ensure healthy growth and longevity of your palm trees, consider the following recommendations:
- Choose the right species: Select a palm tree species that is well-suited to your climate and soil conditions.
- Plant in a sunny location: Palm trees require ample sunlight for optimal growth.
- Water regularly: Water your palm tree deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods.
- Fertilize annually: Fertilize your palm tree with a balanced fertilizer to provide essential nutrients.
- Prune when necessary: Remove dead or damaged leaves to maintain the tree’s health and appearance.

Related image | Brain anatomy, Brain anatomy and function, Brain diagram – Source www.pinterest.com.au
Palm Tree Anatomy: A Closer Look
To appreciate the intricacies of palm tree anatomy, let’s examine each part in more detail:
- Trunk: The trunk of a palm tree is made up of a fibrous network of vascular bundles, which transport water and nutrients throughout the tree. It also contains a central core of soft tissue that stores water.
- Crown: The crown consists of a cluster of leaves that are arranged in a spiral pattern around a central growing point. The leaves are attached to the trunk by a leaf base, which provides support and allows for movement.
- Leaves: Palm tree leaves are typically large and divided into leaflets, which are arranged in a fan-like or feather-like pattern. The leaves are covered with a waxy coating that helps reduce water loss and protect them from UV radiation.
- Roots: Palm trees have a fibrous root system that consists of a network of fine, hair-like roots. This root system helps the tree anchor itself in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.

ArtStation – THE ANATOMY OF A TREE – Source www.artstation.com
Tips for Observing Palm Tree Anatomy
Observing palm tree anatomy can enhance your appreciation for these majestic trees. Here are a few tips:
- Inspect the trunk: Look for the ringed pattern on the trunk, which indicates the age of the tree.
- Examine the crown: Observe the shape and arrangement of the leaves to identify the species of palm tree.
- Handle the leaves: Feel the texture and thickness of the leaves to understand their adaptations to different environments.
- Dig around the roots: Carefully expose a small portion of the roots to see their fibrous nature and how they spread out in the soil.

The anatomy of an oil palm – Source chinadialogue.net
Palm Tree Anatomy: Educational Resources
To further explore the fascinating world of palm tree anatomy, here are some valuable resources:
- Books: “Palms: Their Biology, Utilization, and Cultivation” by John Dransfield and Natalie W. Uhl
- Websites: The International Palm Society (www.palms.org), The Palm Journal (www.palmjournal.com)
- Gardens and Arboretums: Visit botanical gardens and arboretums that feature a diverse collection of palm trees to observe their anatomy firsthand.
Fun Facts about Palm Trees
Palm trees are fascinating trees with many unique characteristics:
- Fastest growing trees: Some palm tree species are among the fastest growing trees in the world, reaching heights of over 100 feet in just a few years.
- Largest leaves: The leaves of the raffia palm (Raphia regalis) can reach lengths of over 80 feet, making them the largest leaves in the plant kingdom.
- Longest lifespan: Some palm tree species can live for over 100 years, with some species even reaching 500 years old.
- Versatile uses: Palm trees have been used for centuries for a variety of purposes, including food, oil, building materials, and religious rituals.
- Air purifiers: Palm trees are effective air purifiers, removing harmful toxins and chemicals from the air.
Parts Of Plant Morphology Of Oak Tree With Green Crow – vrogue.co – Source www.vrogue.co
How to Draw a Palm Tree: Step-by-Step Guide
Capture the beauty of palm trees through art:
- Sketch the trunk: Start with a vertical line for the trunk, adding a slight curve at the base.
- Draw the leaves: Create a cluster of curved lines at the top of the trunk to represent the leaves.
- Add details: Draw individual leaflets on the leaves and add a ringed pattern to the trunk.
- Color and shade: Use light green for the leaves and brown for the trunk, adding shadows to create depth.
What if Palm Trees Could Talk: A Thought Experiment
Imagine if palm trees could speak. What wisdom might they share about the passage of time, the resilience of nature, and the importance of finding balance in life? Their stories could inspire us to appreciate the simple things and to strive for a deeper connection with the natural world.
Listicle: Top 5 Palm Tree Anatomy Surprises
Uncover the unexpected side of palm tree anatomy:
- Hidden water storage: Palm trees can store water in their trunks, which helps them survive in arid environments.
- Waxy leaf coating: The leaves of palm trees have a waxy coating that reduces water loss and protects them from UV radiation.
- Diverse root system: Palm trees have a fibrous root system that can spread out widely, providing stability and access to nutrients.
- Resilient to storms: The flexible nature of palm trees allows them to withstand strong winds and hurricanes.
- Self-cleaning properties: Palm trees shed their old leaves, which helps prevent disease and pests.
Questions and Answers about Palm Tree Anatomy
Resolve